martes, 19 de octubre de 2010
summery 3 food chain and food web
The producer are the one that makes his own food and comsumers are the one that hunt or absorb the food.The producers are the plant and protist and the consummers are the animals,bacteriaand fungi.The herbivore only eats plants and the carnivore eats meet.But is one type of animals that eat the two plants and meat.They are the omnivore.The food chain is the path of food from one organism to another and the food web is the overlapping food chains in the community.
summery 2 living things and their enviroment
The living and nonliving things are part of an the ecosystem. But they are two groups aboitic and biotic.The abiotic factors are the non living things examples :light,water,soil,temperature,minerals and air.And the biotic factors are the living things .EXAMPLES:plants,animals,fungi,protist,and bacteria.Some scientist study ecology to know how the aboitic and biotic factors live or how they interact in the inviroment.
summery1 energy resources
Is two type of energy alternative energy and geothermal energy .All the time we use energy in the day an in the night but in the night we dont use to much energy but in day we use more.In others countries they use the biomass to make fuel that is an example of energy.Brazil is the number one county that use biomass to make fuel . That fuel named gashol that they make with corn.


martes, 28 de septiembre de 2010
earth changing crust
Fault: a crack in the crust, whose sides show evidence of motion.
2.Geologist: a scientist who studies Earth's surface.
3.Magma: hot, molten rock deep below Earth's surface.
4.Lava: magma that reaches Earth's surface.
5.Weathering: the breaking down of rock into smaller pieces.
6.Erosion: the picking up and carrying away of pieces of rock.
7.Deposition: the dropping off of bits of eroded rock.
8.Meteorite: a chunk of rock from space that strikes a surface ( such as Earth or the Moon ).
earth and its neighboors
Solar system: the sun and the objects that are traveling around it.
2.Planet: any of the eight large bodies that travel around the Sun and shine by reflecting it light.
3.Gravity: a force of attraction, or pull, between any object and any other object around it.
4.Inertia: the tendency of a moving object to keep moving in a straight line.
5.Lithosphere:the hard, outer layer of Earth, about 100 kilometers thick.
6.Crust: the rocky surface that makes up the top of the lithosphere.
7.Resource: any material that helps support life on Earth.
8.Hydrosphere: Earth's water.
matter and energy
Kinetic energy: the energy of a moving object.
2.Potential energy: energy stored in an object or material.
3.Conduction: Movement of energy from a hot object that comes into contact with a cooler object; the material remains in place.
4.Convenction: movement of energy by the flow of matter from place to place.
5.Radiation: movement of energy in the form of waves that can travel through empty space.
6.Wet cell battery: a battery containing liquid solution that produces the electricity current.
7.Dry cell batery: a battery that uses "dry chemicals" to produce an electric current.
chemical changes
Phisical change: a change in size , shape , or state , without forming a new substance.
2. Chemical change: a change in matter that produces a new substance with different properties from the original.
3.Chemical reaction: a chemical change of original substances into one or more new substances.
4.Reactant: one of the original substances before a chemical reaction takes place.
5. Product: one of the new substances produced when a chemical reaction takes place.
vocabulary mixture and solucion
Mixture: two or more parts blended together yet keeping their own properties and not turning into a new substance.
2.Solution: a mixture in which substances are completely blended so that the properties are the same throughout and the substances stay blended.
3.Suspension: a mixture of substances that separate upon standing.
4.Colloid: particles ( or droplets ) large enough to block out light spread throughout another substance.
5.Emulsion: a liquid spread through another liquid.
6.Aerosol: liquid dropsor solid particles spread through a gas.
7.Gel: a solid spread through a liquid.
8.Foam: a gas spread through a liquid or solid.
voabulary solids liquids and gases
1.State of matter: any of the forms matter can exist in.
melting point: the temperature at which a solid changes state into a liquid.
3.Boilling point: the temperature at which a liquid changes state into a gas.
4.Freezing point: the temperature at which a liquid changes state into a solid.
vocabulary 6
Element: a basic building block of matter; a pure substance that cannot be broken down into anything simpler.
2.Compound: a chemical combination of two or more elements into a single substance.
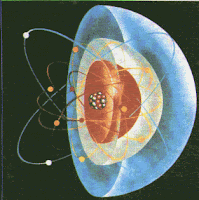
3.Atom: the smallest unit of an element that still has the properties of the element.
4.Proton: a particle with a positive charge in the nucleus of an atom.
5.Neutron: an uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom.
6.Electron: a particle with a negative charge moving around the nucleus of an atom.
7. Nucleus: the dense center part of an atom.
8. Molecule: a group of more than one atom joined together that acts like a single particle.
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)